Bleaching And Whitening Agents
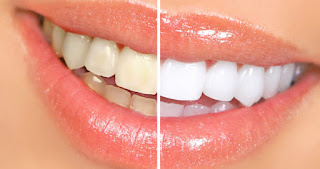
Dental bleaching also known as tooth whitening, is a common procedure in general dentistry but especially in the field of cosmetic dentistry. A child's deciduous teeth are generally whiter than the adult teeth. As a person ages the adult teeth often become darker due to changes in the mineral structure of the tooth, as the enamel becomes less porous. Teeth can also become stained by bacterial pigments, foodstuffs and tobacco. Certain antibiotic medications (like tetracycline) can also lead to teeth stains or a reduction in the brilliance of the enamel.
There are two methods to whiten teeth-bleaching gel and laser bleaching. Traditionally, at-home whitening is done with bleaching gel which is applied to the teeth using thin guard trays. Oxidizing agents such as hydrogen peroxide or carbamide are utilised to lighten the shade of the tooth. The oxidizing agents oxidize the porosities in the rod-like crystal structure of interprismatic stain deposits; over a period of time, the dentin lying underneath the enamel is also bleached. Laser bleaching utilizes light energy to accelerate the process of bleaching in a dental clinic. The effects of bleaching can last for several months, but may vary depending on the lifestyle of the patient. Factors which will decrease whitening include smoking and the ingestion of dark coloured liquids like coffee, tea and red wine.
Internal staining of dentin can discolour the teeth from inside out. Internal bleaching can remedy this. If heavy staining or tetracycline damage is present on a patient's teeth and whitening is ineffective, there are other methods of whitening teeth. Bonding, when a thin coating of composite material is applied to the front of a person's teeth and then cured with a blue light. This can be performed to mask the staining. A veneer can also mask tooth discolouration.
The mechanism of bleaching involves free radicals and breakdown of pigment whereas whitening is accomplished by abrasive action as in dentrifices. Tooth bleaching agents may be used for external or internal bleaching performed in the clinic by a dentist or at home by a patient.
Internal bleaching
Internal bleaching procedures are performed on devitalized teeth that have undergone endodontic therapy but are discoloured due to internal staining of the tooth structure by blood and other fluids. Unlike external bleaching which brightens teeth from the outside in, internal bleaching brightens teeth from the inside out. Bleaching the tooth internally involves drilling a hole into the pulp chamber, cleaning, sealing and filling the root canal with a rubber- like substance, and placing a peroxide gel into the pulp chamber so that the gel can work directly inside the tooth on the dentin layer. Internal bleaching is always performed in the dental clinic. Seldom produces reliable results when used to eliminate intrinsic stains in dentin. There are two common approaches to internal bleaching:
- Office bleach: The agent here is a mixture of 30% to 35% hydrogen peroxide and sodium perborate which is heated to accelerate the process of bleaching.
- Walking bleach: A mixture of hydrogen peroxide and sodium perborate are sealed to the tooth for 2-3 days .
Mechanism of action: Sodium perborate powder decomposes into sodium metaborate and hydrogen peroxide thus releasing nascent oxygen. The sodium perborate powder that is mixed with hydrogen peroxide also releases nascent oxygen. This combination is thought to be synergistic and very effective in bleaching.
Extrinsic bleaching
Is indicated for teeth that are discoloured from ageing, fluorosis or tetracycline staining. It can be applied by the dentist or by the patient. Dentist applied bleaching can be divided into:
- Power bleach with high concentrations of hydrogen peroxide which are premixed gels or liquid bleach with powder system that are mixed chairside. These products are caustic and thus should be cautiously used .
- Assisted bleaching with high concentrations of carbamide peroxide.
Whitening Agents
Various chemical and physical agents can be used to whiten teeth. Toothpaste typically has small particles of silica, aluminum oxide, calcium carbonate or calcium phosphate to grind off stains formed by coloured molecules that have lodged onto the teeth from food. Unlike bleaches, whitening toothpaste does not alter the intrinsic colour of teeth. Bleaching solutions contain peroxide which bleaches the tooth enamel to change its colour. Off-the-shelf products typically rely on a carbamide peroxide solution varying in concentration from 10% to 22%. Bleaching solutions may be applied directly to the teeth, embedded in a plastic strip that is placed on the teeth or use a gel held in place by a mouthguard. Because the concentration is less to avoid toxicity, whitening often takes several weeks.
Whitening treatments used by dentists are much more concentrated, containing substances with more than 30% hydrogen peroxide and require protection of the soft tissues.
Source :- https://www.ida.org.in/Membership/Details/BleachingAndWhiteningAgents
Source :- https://www.ida.org.in/Membership/Details/BleachingAndWhiteningAgents
Dr. Jyoti Chipade is a very experienced dentist in Indore, she provides her services at Aaradhya Dental Care Clinic Indore. She provides Sports Dentistry, Bridal Dentistry, Dental Implant Fixing, Cosmetic Dentistry, Gum Disease Treatment / Surgery, Discolored Tooth Restoration, and Crowns and Bridges Fixing etc. If you are troubled by the problem of your teeth, then Contact Jyoti Chipde. Book an appointment today call now us 8226051989, 7389501402 and visit for more information - http://www.indoredentist.com/
Request an Appointment / General Inquiry :- http://www.indoredentist.com/ContactUs.htm
Please go through our social media :
like our page to know more about Dentist
Please do follow on Instagram
Instagram :- https://www.instagram.com/aaradhyadentalcare/
More post:- Keeping your teeth clean!



Comments
Post a Comment